The air blasting process is a technique offering precision and versatility for handling complex and large components. This guide delves into the air blasting process, outlining its operation, advantages, and applications, and underscores the importance of expert involvement for achieving unparalleled results.
Understanding air blasting process
Air blasting utilizes compressed air to propel abrasive particles against surfaces for various purposes like cleaning, descaling, or preparing for subsequent treatments. Unlike wheelblasting, air blasting offers manual control, making it suitable for intricate, large, or uniquely shaped components. While generally considered less productive due to its manual nature, air blasting shines in delivering unit-specific precision, particularly crucial for complex assemblies and structures such as frames, chassis, and wind turbine components.
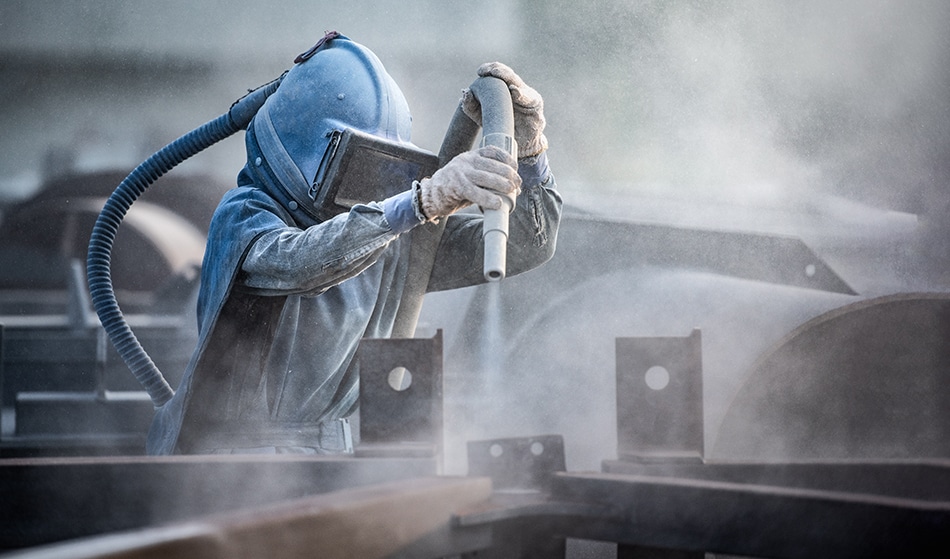


Operational variants and their applications
Air blasting can be executed in two primary modes, depending on the application's specific needs:
- Pressure mode (overpressure): Ideal for ferrous surface preparation, this mode employs abrasives like steel grit, corundum, cast iron, and stainless steel slag to aggressively clean and profile surfaces. Commonly used in larger cabins, pressure mode maximizes efficiency and effectiveness for robust surface preparation.
- Suction mode: Tailored for more delicate or sensitive surfaces, suction mode is gentler, making it suitable for materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and even glass or carbon. Utilizing finer abrasives, this method is predominantly applied in smaller cabins where precision and surface integrity are paramount.
The necessity of dedicated air compressed networks
A dedicated air compressed network is vital for the air blasting process, ensuring consistent pressure and flow, which are crucial for achieving uniform treatment results. This setup must be carefully calibrated and maintained to accommodate the varying demands of different abrasives and support materials.
Choosing the right abrasives for air blasting
The selection of abrasives in air blasting is diverse, catering to different substrates and desired finishes:
Angular abrasives (GH/GL): Used for aggressive cleaning and surface preparation, these abrasives are suitable for creating a profile that enhances coating adhesion.
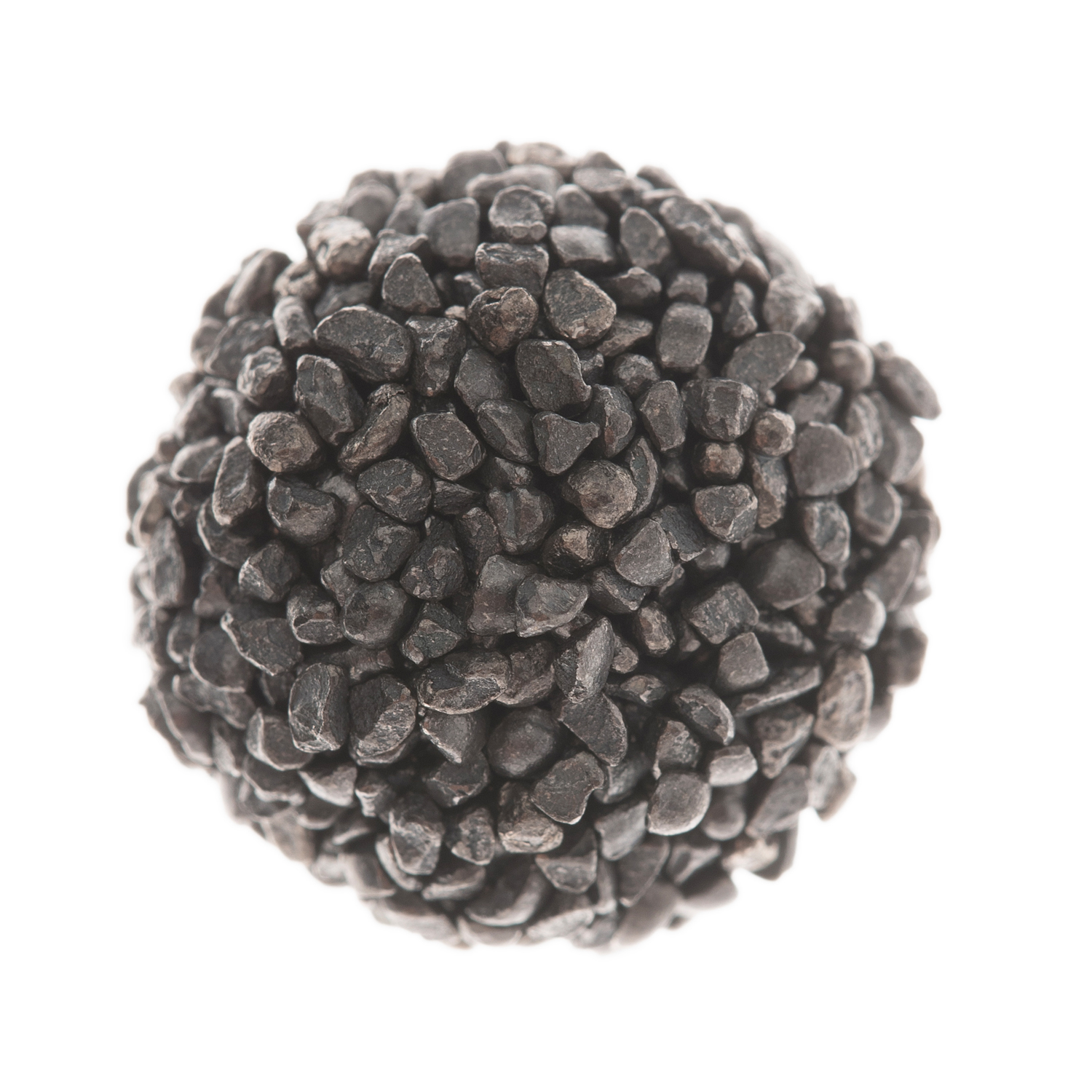


Stainless steel grit (Stelux CG): Preferred for applications demanding cleanliness and minimal ferrous contamination, especially in industries like food processing or medical equipment manufacturing.
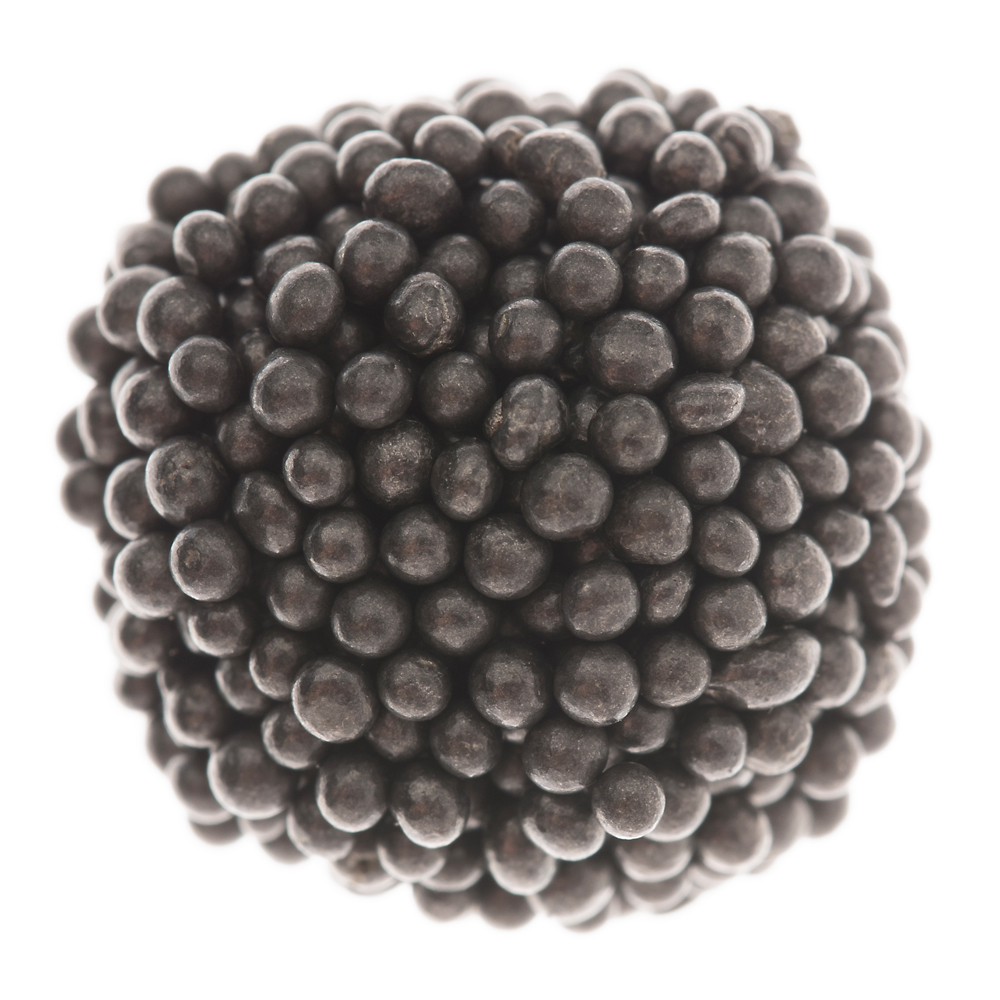


Specialty media for shot peening: In applications requiring surface stress relief or hardening, round abrasives like steel shot or conditioned cut wire are employed to deliver consistent peening intensity.
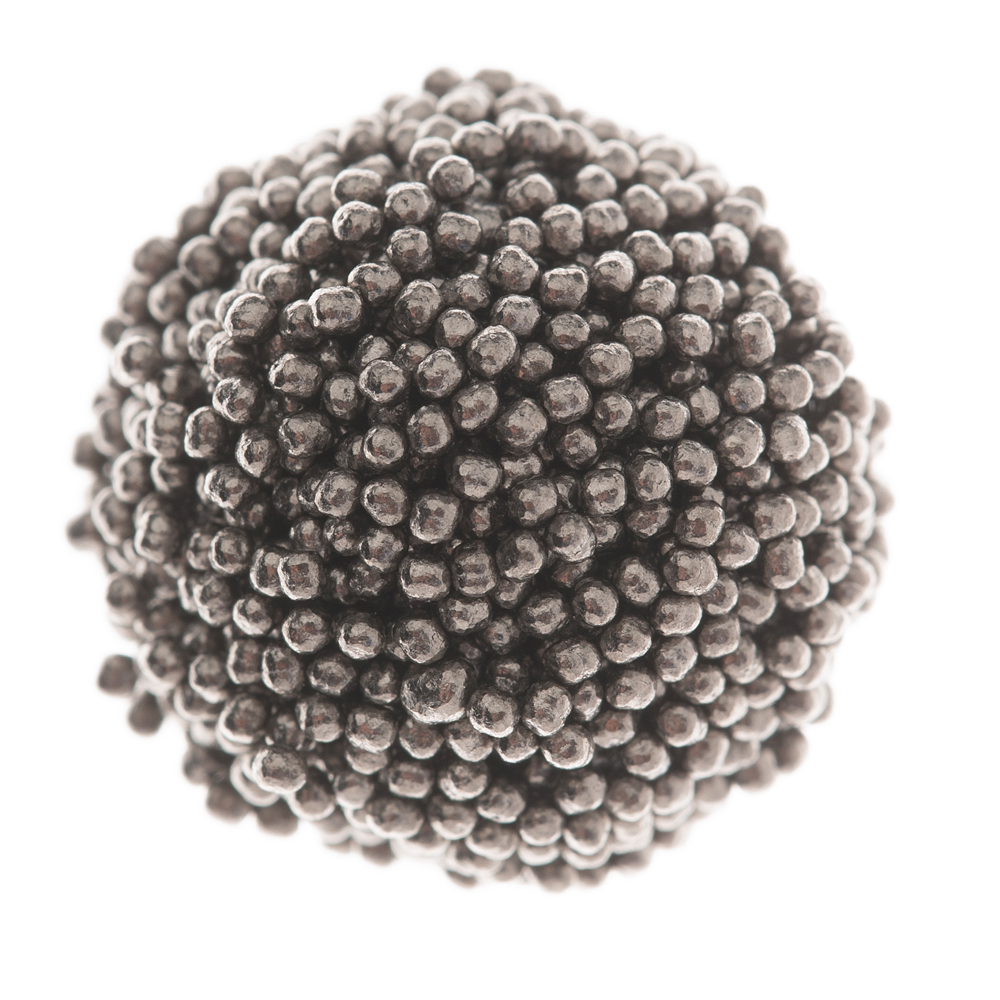

The role of expert guidance
Expert guidance is indispensable in the air blasting process, from selecting the appropriate abrasive media and equipment to customizing operational parameters for specific applications. Specialists can provide insights into the nuances of air blasting, ensuring that each project benefits from the optimal combination of media, pressure, and technique. This expertise not only enhances the process efficiency but also ensures that the results meet the stringent quality standards required by various industries.
Conclusion
The air blasting process is a component of modern surface treatment, valued for its adaptability and precision. By understanding the intricacies of this method and leveraging expert advice, professionals can harness the full potential of air blasting for a wide array of applications, achieving exceptional surface quality and preparing substrates for further processing or finishing. Whether dealing with large, complex structures or requiring meticulous attention to detail, air blasting offers a tailored solution that upholds the industry standards.